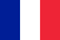
Foot fungus is a skin disease that manifests itself with the active multiplication of certain types of fungi in the epidermis. Today, both adults with weakened immune systems and children are susceptible to this disease. The signs of fungus on the feet depend on the type of pathogen of the infectious process and the volume of the affected foot and nail plate and at different stages have certain differences, which indicates the progression of the infection. You need to know how to recognize the fungus on your feet, which will allow you to start timely treatment and stop its further development.

Symptoms of the disease
The main place for the development of fungus on the feet most often becomes the area between the toes. This pathology is accompanied by the appearance of symptoms such as burning, severe itching and redness of the epidermis. In addition, a person may experience cracking and flaky skin, as well as blistering of the feet and increased dryness of the dermis.
The same symptoms of foot fungus can appear on the sole and are accompanied by excessive keratinization of the skin. The insidiousness of such a disease lies in the fact that during its course it is possible the formation of difficult to treat fungus on the feet, and the wounds themselves are in a state of superinfection.
How to recognize the fungus on the feet and what symptoms can signal the onset of the disease? The first signs of the disease are the appearance of small scales, ie different types of peeling, ranging from small pityriasis to large lamellae. There are different types of fungi that provoke the development of the disease, but they are all characterized by the same symptoms:
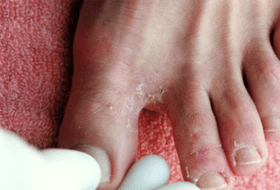
- In the initial stage of its development, the pathology proceeds without the appearance of pronounced symptoms. The interdigital folds are affected in the first place, and most often between the third and fourth fingers.
- As the fungal disease progresses, the sides of the feet are affected and gradually spread to the ankle.
- With a fungal infection of the feet, the skin noticeably thickens, cracks and begins to shine.
- The skin becomes too dry and begins to itch a lot. In addition, the epidermis becomes very red and its affected areas become inflamed.
- Patients begin to complain of pain and burning in the legs.
- As the disease progresses to a neglected form, blisters begin to appear on the skin. When they are opened, the affected areas of the skin become very wet and soft.
There are several forms of fungus on the feet and each of them is accompanied by the development of certain symptoms.
Forms of pathology
Experts have identified the following types of fungi that can affect the skin of the feet:
- interdigital;
- hyperkeratotic (moccasin);
- dyshydrotic.
The most common form of interdigital fungus on the feet is interdigital, which is characterized by the appearance of certain signs:
- most often the site of localization of this form of fungus becomes the area of the fourth and fifth toes.
- as the disease progresses, the skin acquires a characteristic scaly appearance and may crack severely;
- between 3, 4 and 5 a weeping crack or funnel is formed, which is surrounded by flakes of dried skin of white or green color.
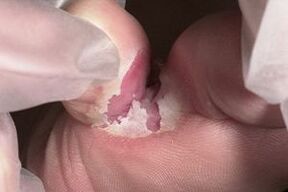
Interdigital fungal skin lesions can be both dry and wet. If a wet interdigital fungus is found, the skin appears swollen. In dry lesions of the epidermis, its peeling and discoloration is noted.
The first sign of fungus on the feet, similar to moccasins, is pain, the manifestation of which is observed in the foot. As the pathology progresses, there is a gradual thickening of the skin of the sole, which causes the formation of cracks.
This form of fungal disease of the feet is considered the most difficult and neglected, but it is easy to recognize. Fungal disease can manifest itself in the defeat of the nail plates, in which case they acquire a characteristic thickening, tend to disintegrate and may even fall out completely.
The vesicular form of the fungus is characterized by the formation of blisters inside which there is clear fluid. Gradually, such bubbles mature, become cloudy and open, which causes the formation of erosions of various sizes. The main location of the bubbles becomes the area closer to the toes, but it is possible that they shave all over the moccasin.
The vesicular form of fungal disease is considered quite rare, but much easier to treat. This is due to the fact that the vesicles become the site of localization of the pathogen, ie it does not penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin. When a viral or fungal infection is associated with a vesicular fungal disease, serious skin lesions are observed and treatment becomes difficult.
Specialists distinguish an erased form of the fungus on the feet, in which all symptoms are blurred. Diagnosing such pathology is quite problematic, as the affected skin looks like ordinary untidy legs. In a patient with such a foot fungus, the symptoms are yellowing of the nails and flaking of the feet, but they are so mild that the patient does not pay attention to them.
The erased form of the fungus flows in waves, ie in the hot season it worsens, and in winter it almost completely disappears. With each weakening of the immune system there is a sharp exacerbation of the disease, which creates difficulties in the treatment of fungus on the feet.
How to recognize onychomycosis?
Signs of nail fungus can vary greatly at different stages, signaling the progression of the infection. How do toenail fungus start and what signs should I watch out for?
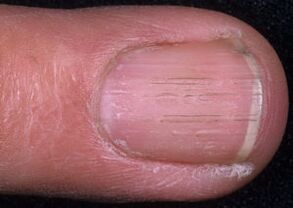
- In the first stage there are no characteristic symptoms of the lesion and barely noticeable streaks and spots appear on the nail. If you ignore the first signs of the disease and start the fungus, then the accumulation of pus in the area of the nail plates is possible. The result of such a pathological process is gangrene or amputation of the lower limbs.
- In the second degree of fungal disease, the natural shine of the nails disappears. Gradually the nail changes color and white and brown streaks form on it. Deformation of the upper part of the nail and its lateral parts is possible. The advanced stage of bacterial damage to the nails is characterized by their increased fragility, delamination and inflammation of the cuticle. The pathology continues to progress and spreads to other nails and feet.
- In the third stage of onychomycosis, the nail becomes yellow or dirty brown. In addition, it becomes too loose, thickens and lags behind the nail bed. Often when wearing shoes, severe pain begins and the itchy skin becomes simply unbearable.
There are several types of fungal infections of the toenails, each of which causes certain symptoms.
- Hypertrophic onychomycosis is accompanied by thickening of the nail and its yellowing. The nail crumbles well and a thickened epidermis can be seen under it.
- Atrophic onychomycosis causes thinning of the nail and its destruction, and keratinized skin can be seen under it.
- Onychomycosis, when affected by moldy fungi, often develops not as an independent disease, but against the background of other pathologies.
The nail can be colored yellow, brown, green or black. A complication often develops in the form of inflammation of the nail bed with pus.
Prevention of pathology

With the normal functioning of the immune system, it is unlikely that nail fungus will start to develop after an infection, as the body can handle it on its own. If the fungal infection still affects the feet and nails, then it is necessary to undergo effective treatment. The earlier the fight against such pathology begins, the greater the patient's chances of complete recovery.
Fighting foot fungus is considered to be quite a difficult process, so it is easier to prevent the development of the disease. To do this, you must observe the following preventive measures:
- keep your feet dry;
- do not wear other people's shoes;
- choose socks to be made of cotton fabric;
- Do not run barefoot on the beach.
When the first signs of foot fungus appear, you should contact a specialist. It is important to identify the pathology at the very beginning of its development and to prevent further progression, which will help avoid many complications. To find out how to identify foot fungus, you should consult a dermatologist.